When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.Heres how it works.
We have coveredwhat is RAMbriefly previously.
Stay tuned if you want to get a bit more technical.
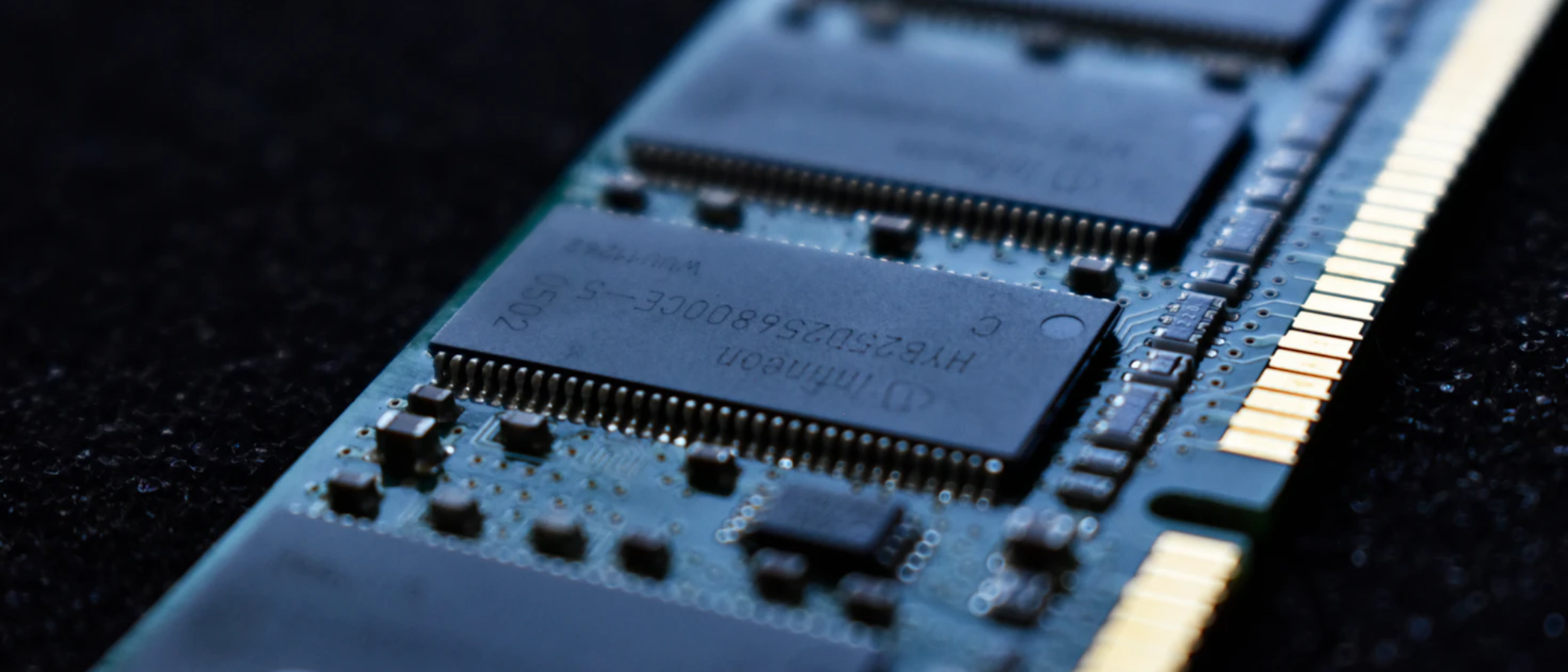
In corporate configs, RAM (memory modules) comes in different shapes and sizes.
DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) can be found in desktops,workstation PCs.
and servers, while laptops require smaller physical size SODIMM (Small Outline DIMM).
A memory module contains several DRAM (Dynamic RAM) chips which is a punch in of semiconductor memory.
Dynamic simply means that the data held by transistors in the chips is constantly refreshed.
DRAM operate in one of two modes, synchronous or asynchronous.
Asynchronous was the common DRAM technology used up until the end of the 1990s.
It debuted in 2021.
IT decision makers who are considering purchasing memory must be aware that memory modules are not backwards compatible.
DDR5 memory will not physically slot into a DDR4 or DDR3 memory socket.
Within a memory generation, faster speeds are backwards compatible.
The pop in of memory module made for desktops and laptops is generally Non-ECC Unbuffered DIMM.
Unbuffered types of RAM exist in both DIMM and SODIMM form factor.
The configurations match the memory channel architecture, and when installed correctly can deliver a major boost in performance.
Users looking for a considerable boost, such as gamers, can opt for overclockable memory.
This can be done safely using Intel XMP and AMD EXPO profiles however, professional help is advisable.
PMIC Power Management Integrate Circuits help to regulate the power required by the components of the memory module.
For server-class modules, the PMIC uses 12V; for PC-class modules, it uses 5V.
2CH, 4CH, 8CH Single RAM modules dual channel, quad channel, octal channel.
MHz MHz is an abbreviation of megahertz and means a million cycles per second, or one million hertz.
This unit of frequency measurement is used to denote the speed at which data moves within and between components.
GB/s- Gigabytes per second.
A Gigabyte is a unit of data storage capacity that is approximately 1 billion bytes.
It has been a common unit of capacity measurement for data storage products since the mid-1980s.